Math for Computer Science: Breaking down barriers to early computer science education
/
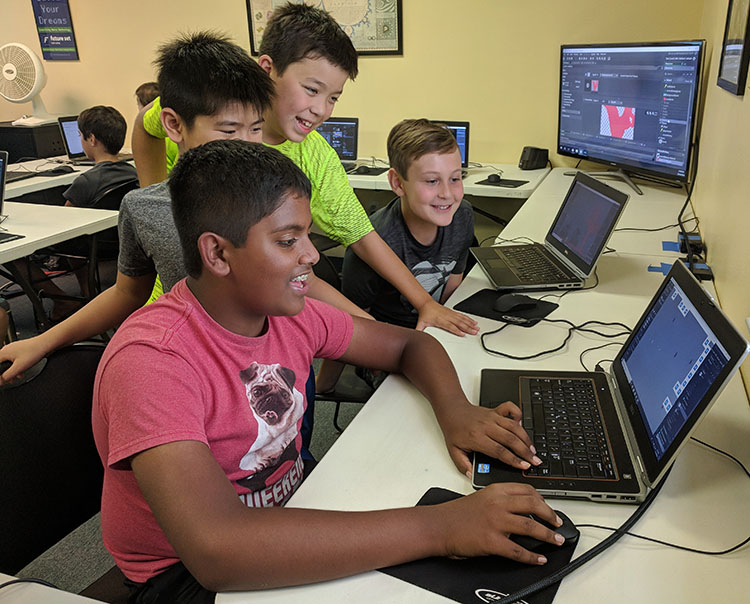
Eric Bennett, M.Ed., directs Future Set Tech Camp, where creativity meets technology in project-based STEM summer camps, Saturday workshops, and after-school programs. He joins us on the blog to explain why he created a free online Math for Computer Science course for kids.
The idea that elementary-aged children will benefit from a course on a buzzy programming language is certainly appealing to well-intentioned parents: understanding the world around us increasingly means understanding technology; jobs in software engineering and information technology are both high-paying and in-demand; many children are naturally curious about technology. The problem with this idea is that writing even the most basic computer program requires an understanding of math concepts beyond the scope of a typical elementary curriculum. If students lack this math knowledge, computer science instruction will not have the intended benefit: students might be able to copy an instructor’s code but will not understand how it works or be able to produce code of their own.
Since math is used so extensively in computer science, is it possible that students will learn it through the process of writing a computer program or developing a video game? While the notion of learning math through games or in the context of a fun project is seductive, the reality is that mathematics is best learned through structured practice. Procedural fluency, as it is termed by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM), is a critical component to teaching mathematics, and fluency is only developed through repetition. Creative applications such as coding or game development will certainly enhance a child’s understanding but cannot replace more rigorous instruction.
For these reasons, mathematics has often been used as a prerequisite for computer science courses: students are allowed to enroll in a computer science course only after completing a particular mathematics course. While this approach ensures that students are prepared to reap the benefits of a computer science course, it also creates a barrier to entry. Thus, whether students simply lack math knowledge or it is enforced as a prerequisite, the benefits of courses in computer programming and video game development are limited for many interested students. Two solutions to this problem are clear: the first would involve selecting computer science curriculum that does not require this math knowledge; the second would be to deliver targeted mathematics instruction to interested students.
Front-end web design involves HTML and CSS, both of which are markup languages rather than programming languages. Just as a word processor can be instructed to adjust font sizes, spacing, and alignment, markup languages can be used to add structure to the words on a web page. While numbers can be used to specify sizes, dimensions, and positions within these markup languages, they cannot be expressed as variables, expressions, or equations. Thus, HTML and CSS are an excellent introduction to computer science for elementary-aged students. However, because most of these students are more interested in creating a fun game than an informative website, this solution may not be ideal.
The math concepts involved in computer programming and video game development are typically taught to older students, so this content should be presented to elementary students in a different way. Visual models and manipulatives are often used to assist struggling students and are promoted by the NCTM for their effectiveness in teaching conceptual understanding. These techniques, then, should serve elementary students well in tackling more advanced math concepts. Additionally, in computer programming, calculations are made by the computer program rather than the computer programmer. For the purposes of computer science readiness, then, tedious fraction and decimal arithmetic can be pushed aside in favor of integer operations and more abstract concepts like variables and variable expressions. For an example of a curriculum constructed according to these principles, check out Future Set Tech Camp’s Math for Computer Science, a free online course.
Rather than using mathematics as a barrier to entry, closing the door to many interested students, we can use computer science to motivate these students to learn specific, carefully presented math concepts. With so many children naturally drawn to technology and our job market’s demand for computer science skills stronger than ever, there are clear benefits in delivering computer science education to elementary-aged students. With the right mathematics and computer science curriculum, these benefits can be fully realized.
Eric Bennett